Kernel Açılış Süreci
Sistem Açılışı
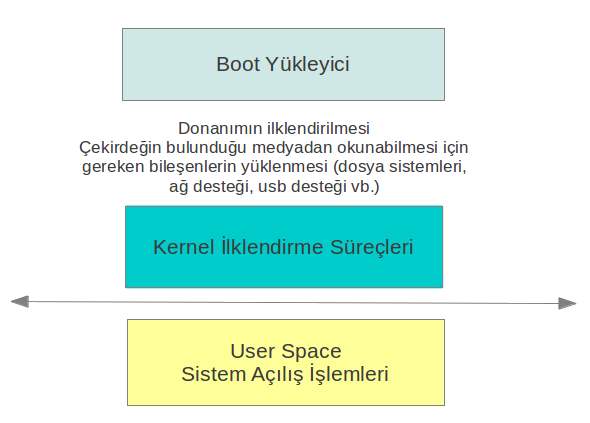
Kernel Bootstrap Süreci
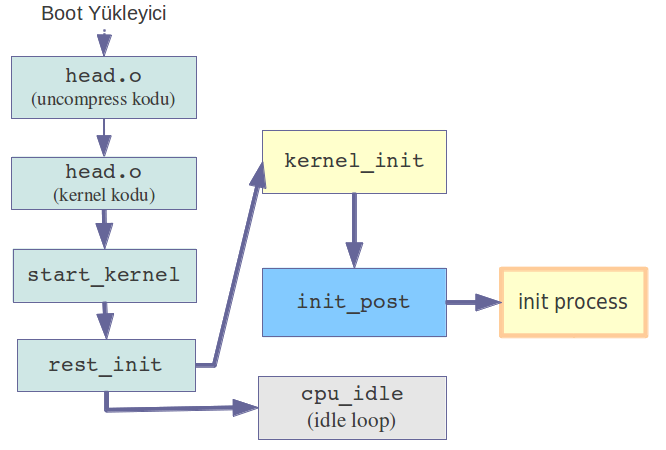
Kernel Derleme İşleminde Son Adımlar
...
LD vmlinux
SYSMAP System.map
SYSMAP .tmp_System.map
OBJCOPY arch/arm/boot/Image
Kernel: arch/arm/boot/Image is ready
AS arch/arm/boot/compressed/head.o
GZIP arch/arm/boot/compressed/piggy.gzip
AS arch/arm/boot/compressed/piggy.gzip.o
CC arch/arm/boot/compressed/misc.o
CC arch/arm/boot/compressed/decompress.o
AS arch/arm/boot/compressed/head_cpu.o
SHIPPED arch/arm/boot/compressed/lib1funcs.S
AS arch/arm/boot/compressed/lib1funcs.o
LD arch/arm/boot/compressed/vmlinux
OBJCOPY arch/arm/boot/zImage
Kernel: arch/arm/boot/zImage is ready
..
Kernel Bootstrap Kodu
- head.o:
Bu bölümde mimariye özgün obje kodları bulunur. Boot yükleyici uygulama tarafından çalıştırılmasına yöneliktir.
- head-cpu.o:
İşlemciye özgü ilklendirme işlemlerine ait kodları barındırır.
- decompress.o:
Sıkıştırılmış formda bulunan kernel'i açma işlemlerini gerçekleştirir.
- lib1funcs.o:
ARM mimarisi için optimize edilmiş bölme işlemlerine dair kodları içerir. VFP NEON
head.o Tarafından Yapılan İşlemler
Mimari, işlemci ve makine/sistem tipinin belirlenmesi
Memory Management Unit konfigürasyonu ve virtual memory desteğinin etkinleştirilmesi
init/main.c içerisindeki start_kernel fonksiyounun çağrılması
start_kernel
asmlinkage void __init start_kernel(void)
{
char * command_line;
extern const struct kernel_param __start___param[], __stop___param[];
smp_setup_processor_id();
/*
* Need to run as early as possible, to initialize the
* lockdep hash:
*/
lockdep_init();
debug_objects_early_init();
/*
* Set up the the initial canary ASAP:
*/
boot_init_stack_canary();
cgroup_init_early();
local_irq_disable();
early_boot_irqs_disabled = true;
/*
* Interrupts are still disabled. Do necessary setups, then
* enable them
*/
tick_init();
boot_cpu_init();
page_address_init();
printk(KERN_NOTICE "%s", linux_banner);
setup_arch(&command_line);
mm_init_owner(&init_mm, &init_task);
mm_init_cpumask(&init_mm);
setup_command_line(command_line);
setup_nr_cpu_ids();
setup_per_cpu_areas();
smp_prepare_boot_cpu(); /* arch-specific boot-cpu hooks */
build_all_zonelists(NULL);
page_alloc_init();
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Kernel command line: %s\n", boot_command_line);
parse_early_param();
parse_args("Booting kernel", static_command_line, __start___param,
__stop___param - __start___param,
&unknown_bootoption);
jump_label_init();
/*
* These use large bootmem allocations and must precede
* kmem_cache_init()
*/
setup_log_buf(0);
pidhash_init();
vfs_caches_init_early();
sort_main_extable();
trap_init();
mm_init();
/*
* Set up the scheduler prior starting any interrupts (such as the
* timer interrupt). Full topology setup happens at smp_init()
* time - but meanwhile we still have a functioning scheduler.
*/
sched_init();
/*
* Disable preemption - early bootup scheduling is extremely
* fragile until we cpu_idle() for the first time.
*/
preempt_disable();
if (!irqs_disabled()) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "start_kernel(): bug: interrupts were "
"enabled *very* early, fixing it\n");
local_irq_disable();
}
idr_init_cache();
perf_event_init();
rcu_init();
radix_tree_init();
/* init some links before init_ISA_irqs() */
early_irq_init();
init_IRQ();
prio_tree_init();
init_timers();
hrtimers_init();
softirq_init();
timekeeping_init();
time_init();
profile_init();
call_function_init();
if (!irqs_disabled())
printk(KERN_CRIT "start_kernel(): bug: interrupts were "
"enabled early\n");
early_boot_irqs_disabled = false;
local_irq_enable();
/* Interrupts are enabled now so all GFP allocations are safe. */
gfp_allowed_mask = __GFP_BITS_MASK;
kmem_cache_init_late();
/*
* HACK ALERT! This is early. We're enabling the console before
* we've done PCI setups etc, and console_init() must be aware of
* this. But we do want output early, in case something goes wrong.
*/
console_init();
if (panic_later)
panic(panic_later, panic_param);
lockdep_info();
/*
* Need to run this when irqs are enabled, because it wants
* to self-test [hard/soft]-irqs on/off lock inversion bugs
* too:
*/
locking_selftest();
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INITRD
if (initrd_start && !initrd_below_start_ok &&
page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)) < min_low_pfn) {
printk(KERN_CRIT "initrd overwritten (0x%08lx < 0x%08lx) - "
"disabling it.\n",
page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)),
min_low_pfn);
initrd_start = 0;
}
#endif
page_cgroup_init();
enable_debug_pagealloc();
debug_objects_mem_init();
kmemleak_init();
setup_per_cpu_pageset();
numa_policy_init();
if (late_time_init)
late_time_init();
sched_clock_init();
calibrate_delay();
pidmap_init();
anon_vma_init();
#ifdef CONFIG_X86
if (efi_enabled)
efi_enter_virtual_mode();
#endif
thread_info_cache_init();
cred_init();
fork_init(totalram_pages);
proc_caches_init();
buffer_init();
key_init();
security_init();
dbg_late_init();
vfs_caches_init(totalram_pages);
signals_init();
/* rootfs populating might need page-writeback */
page_writeback_init();
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
proc_root_init();
#endif
cgroup_init();
cpuset_init();
taskstats_init_early();
delayacct_init();
check_bugs();
acpi_early_init(); /* before LAPIC and SMP init */
sfi_init_late();
ftrace_init();
/* Do the rest non-__init'ed, we're now alive */
rest_init();
}
setup_arch(&command_line)ile bootloader tarafından spesifik bir adrese konulmuş olan kernel boot parametrelerini işlerMesajları olabildiğince erken gösterebilmek için console aygıtının ilklendirilmesi
security, buffers, high resolution timers gibi bir çok altsistemin ilklendirilmesi
Son olarak
rest_init'in çağrılması
rest_init
init sürecinin her zaman PID değeri olarak 1 alması için erkenden bir thread oluşturuluyor ve idle_loop'a geri dönüyor:
static noinline void __init_refok rest_init(void)
{
int pid;
rcu_scheduler_starting();
/*
* We need to spawn init first so that it obtains pid 1, however
* the init task will end up wanting to create kthreads, which, if
* we schedule it before we create kthreadd, will OOPS.
*/
kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_SIGHAND);
numa_default_policy();
pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);
rcu_read_lock();
kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns);
rcu_read_unlock();
complete(&kthreadd_done);
/*
* The boot idle thread must execute schedule()
* at least once to get things moving:
*/
init_idle_bootup_task(current);
preempt_enable_no_resched();
schedule();
/* Call into cpu_idle with preempt disabled */
preempt_disable();
cpu_idle();
}
kernel_init
kernel_init temel olarak iki çağrıda bulunur:
Bu aşamada temel kernel servisleri hazır olduğundan, device init işlemlerini başlatmak amacıyla
do_basic_setupçağrılır!c static void __init do_basic_setup(void) { cpuset_init_smp(); usermodehelper_init(); shmem_init(); driver_init(); init_irq_proc(); do_ctors(); usermodehelper_enable(); do_initcalls(); }Sonrasında
init_postçağrılır
init_post
Boot işleminin son adımlarını gerçekleştirmekten sorumludur.
Bir console açmayı dener (Initial Console)
Başarısız olduğu takdirde:
Unable to open initial consoleuyarı mesajı görüntülenir.Ardından
initprocess'ini çalıştırmayı dener.Başarılı olması halinde rest_init sürecinde oluşturulan kernel thread'ini bir userspace process'e dönüştürür.
init_post
static void run_init_process(const char *init_filename)
{
argv_init[0] = init_filename;
kernel_execve(init_filename, argv_init, envp_init);
}
static noinline int init_post(void)
{
/* need to finish all async __init code before freeing the memory */
async_synchronize_full();
free_initmem();
mark_rodata_ro();
system_state = SYSTEM_RUNNING;
numa_default_policy();
current->signal->flags |= SIGNAL_UNKILLABLE;
if (ramdisk_execute_command) {
run_init_process(ramdisk_execute_command);
printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to execute %s\n",
ramdisk_execute_command);
}
/*
* We try each of these until one succeeds.
*
* The Bourne shell can be used instead of init if we are
* trying to recover a really broken machine.
*/
if (execute_command) {
run_init_process(execute_command);
printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to execute %s. Attempting "
"defaults...\n", execute_command);
}
run_init_process("/sbin/init");
run_init_process("/etc/init");
run_init_process("/bin/init");
run_init_process("/bin/sh");
panic("No init found. Try passing init= option to kernel. "
"See Linux Documentation/init.txt for guidance.");
}
Özet
Boot yükleyici uygulaması tarafından bootstrap kodu çalıştırılıyor
Bootstrap kodu işlemci ve kartı ilklendiriyor
Ardından Linux kernel'i RAM bellek üzerinde uncompress ediyor.
start_kernel fonksiyonu çalıştırılıyor
Boot yükleyici tarafından sağlanan command line bölümü kopyalanıyor
Sistem ve konsol ilklendirmeleri yapılıyor
Temel kernel servisleri ilklendiriliyor
İleride
initprocess'ine dönüşecek kernel thread'i oluşturuluyorAygıtlar ilklendiriliyor ve
initprocess'i userspace'ten çalıştırılıyor.